In this week's Abundance Insider: Self-organizing drone swarms, synthetic stem cells, and an AI that can detect heart failure better than human doctors.
Cheers,
Peter, Marissa, Cody, Kelley, Greg, Sydney and AJ
P.S. I'm launching an online course with SUCCESS Magazine called Xponential Advantage. It's aimed to inspire, educate and guide a new breed of "Exponential Entrepreneurs," and is an expansion of my core content from Abundance and BOLD, the keynotes I give to Fortune 500 executive teams, and some of the material I teach executives who attend Singularity University. These are the areas I truly believe an exponential entrepreneur can leverage to have a billion-person impact. Learn more about the course here.
Artificial Intelligence Can Now Predict Heart Failure
What it is: Scientists at the London Institute of Medical Services have created an AI capable of predicting with 80% accuracy which patients would die of pulmonary hypertension within a year, beating the average doctor's prediction accuracy by about 20%. The system was trained on eight years of patient records and tracks over 30,000 points on beating hearts to create its 3D scans, enabling it to more accurately diagnose the severity of a patient's condition than with traditional methods.
Why it's important: This AI represents another promising use case of machine learning and artificial intelligence for healthcare. (You may recall that last July, Google announced that DeepMind's AI would diagnose macular degeneration; a month earlier, Harvard researchers demonstrated a system for detecting breast cancer with 92% accuracy.) As these AIs have access to exponentially larger and more diverse data sets, look for improved accuracy and application to other areas of healthcare. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Marissa Brassfield / Written by Jason Goodwin
A 100-Drone Swarm, Dropped from Jets, Plans Its Own Moves
What it is: U.S. military officials have just carried out their largest-ever test of a drone swarm released from three fighter jets in flight. The three F/A-18 Super Hornets released 103 Perdix drones. What's especially interesting about this test is that the drones were not preprogrammed -- instead, every Perdix is meant to communicate and collaborate with every other Perdix through collective activities. Based on the inexpensive, lightweight and small characteristics of the Perdix, they're the ideal drone to drop from jets to perform missions that would usually require much larger drones.
Why it's important: As Peter mentioned in his blog on Drones and Technology Convergence, built-in next-generation sensors and high-bandwidth communications have made drones an effective data-gathering platform. Soon, further advances in exponential technologies, batteries and material sciences will make drones smart, cheap, reliable, scalable (both small and large), and ultimately ubiquitous. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Marconi Pereira / Written by Sydney Fulkerson
Researchers Use Stem Cells to Regenerate the External Layer of a Human Heart
What it is: A Penn State research team led by Xiaojun Lance Lian has created a process using human stem cells that can generate epicardium cells, or the cells that cover the external surface of a human heart. This discovery confirmed that activating the cells' Wnt -- a group of signal transduction pathways made of proteins that pass signals into a cell using cell-surface receptors -- can re-drive these cardiac progenitor cells to become epicardium cells, instead of myocardium cells (the middle of the heart that drives blood through the body). This process represents a key milestone in the team's overall goal to regenerate an entire heart wall.
Why it's important: As Peter mentioned in his recent blog Stem Cell Revolution, the use of the body's own stem cells to repair, replace or augment diseased tissue has the potential to change medicine forever, extend life and potentially save your life. When we're able to regenerate heart walls, we enable unprecedented solutions to heart disease treatment and prevention (for example, epicardium cell transplants). Join the Discussion
Spotted by Aryadeep S. Acharya / Written by Sydney Fulkerson
Technique Enables Adaptable 3D Printing
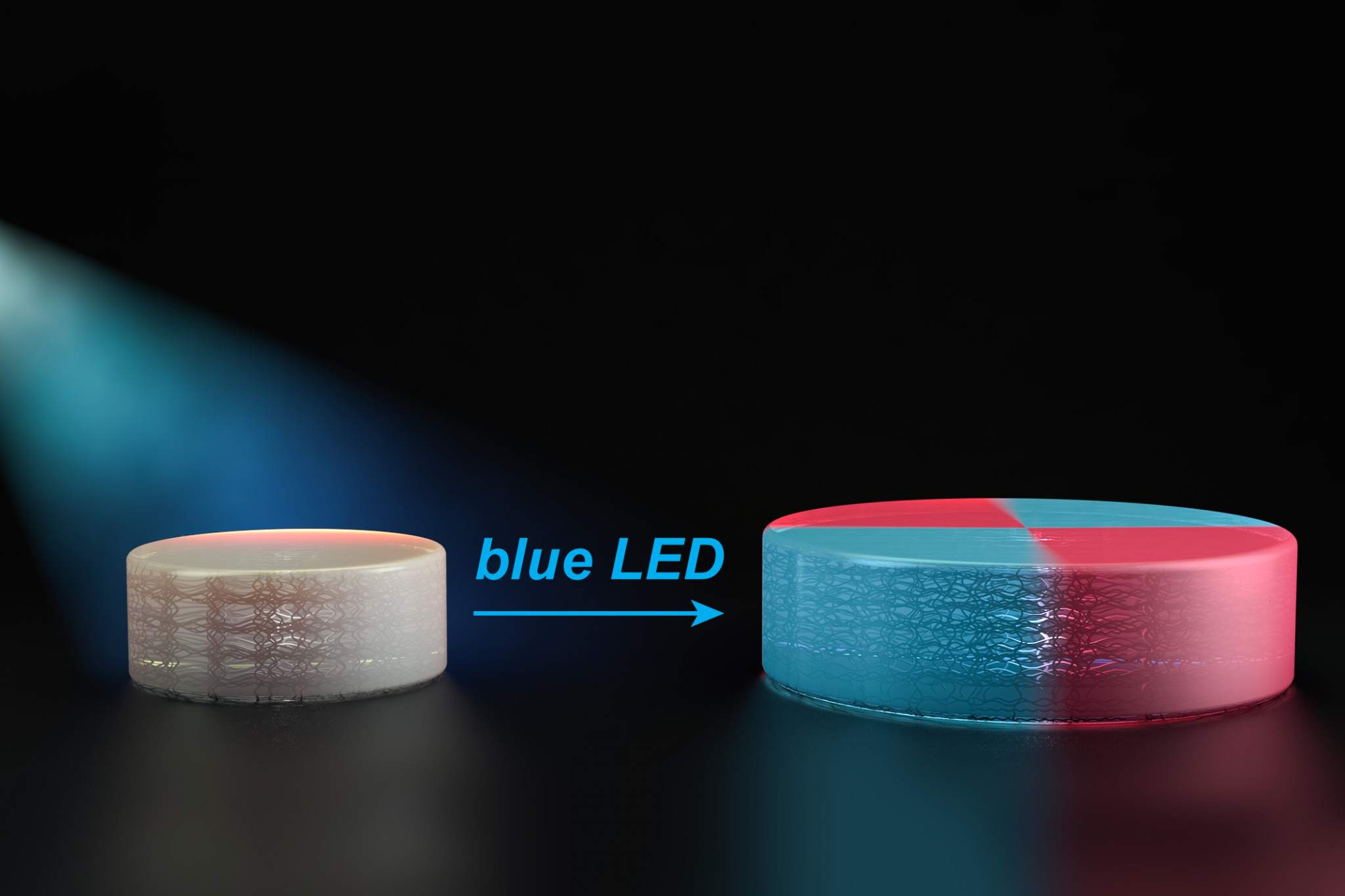
What it is: A group of MIT chemists developed a new adaptable 3D printing technique that crushes the notion that polymers cannot be extended to form new polymer chains. These new polymers can be reactivated by blue LED light, enabling users to manipulate and redesign the objects. The ability to print a material and subsequently use light to morph the material or grow the material further could greatly expand the complexity and functionality of 3D printed objects.
Why it's important: This adaptable 3D printing technique comes from the convergence of materials science and polymer science, and enables us to 3D print objects and change their properties without redesigning and printing new prototypes after each iteration. One of the top anticipated 3D printing breakthroughs Peter has described is a 'Factory in a Box' -- the combination of additive and subtractive manufacturing, which would deliver 100x speeds through machining, additive layering and even injection molding. As 3D printing capabilities evolve, this "factory of the future" will dematerialize, demonetize and democratize manufacturing, turning us all into creators. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Marissa Brassfield / Written by Sydney Fulkerson
Biocompatible Microrobots That Can be Implanted Into the Human Body
What it is: Engineers at Columbia University have created microrobots that are both implantable in the human body and controllable wirelessly via magnetic iron particles embedded in the device. Working with biocompatible hydrogels, the team invented a new technique for stacking the materials in layers, overcoming the inability to use traditional machining methods. The team then successfully used the the device to deliver a highly targeted dose of chemotherapy to mice with bone cancer, reducing tumor growth with far less toxicity.
Why it's important: Most current micro-devices require batteries or other toxic electronics, limiting their biocompatibility. Overcoming many of these challenges, the team opens up potential applications ranging from catheters to pacemakers, sensors and drug delivery. Imagine a future where such soft robots are able to not only treat disease, as in this example, but also detect and monitor the state of various systems noninvasively. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Cody Rapp / Written by Jason Goodwin
Synthetic Stem Cells Offer Benefits of Natural Stem Cells Without the Risks
What it is: Scientists at NC State, UNC Chapel Hill, and First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University in China have created the first synthetic cell-mimicking microparticle, capable of delivering growth and regenerative factors like a stem cell. In a mouse model, the microparticles were able to promote growth and repair after myocardial infarction similar to a real stem cell, but without the risk of immune rejection or tumor growth. The particles also have better preservation stability than natural stem cells, withstanding harsh freezing and thawing cycles.
Why it's important: As the authors note, although the first application targeted the heart, this type of microparticle is a platform that can be used with other organ systems. In the near future, look for expanded use of stem cell therapies for cellular rejuvenation in the event of disease or organ failures. Longer term, we'll be able to apply this cellular rejuvenation to otherwise healthy but aging systems, enabling radical life extension. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Aryadeep S. Acharya / Written by Jason Goodwin
14-Year-Old Indian Schoolboy Signs Government Contract to Make Anti-Landmine Drones

What it is: Fourteen-year-old Harshwardhan Zala has signed a deal to produce anti-landmine drones with the Government of Gujarat's Department of Science and Technology, a contract worth about $733,000. The 10th grader from India presented the drone prototype in 2016, which cost about $7,300 to make with partial financing from the government. Zala said the idea came to him after learning in the media about the high army casualties caused by landmines. The drones will contain infrared and RGB sensors, a thermal meter, and a 21-megapixel camera with a mechanical shutter for high-resolution image capturing. The Gujarat government hopes that these anti-landmine drones will eventually be commercially produced.
Why it's important: One of the next big breakthroughs in drone research and development will be "sense-and-avoid." Just as Harshwardhan's goal for his drone is to detect landmines using sensors and cameras, drones will "need to have eyes," as explained by Chris Anderson, CEO of 3D Robotics. "They'll need to use [sensors] to autonomously avoid obstacles and fly. It's environmental awareness and it is necessary to safely navigate worlds they've never explored. Eventually, the data from autonomous drones will convince the regulators that they're safer than having a pilot." Join the Discussion
Spotted by Dan Swift / Written by Sydney Fulkerson
Robot Cars Can Learn to Drive Without Leaving the Garage

What it is: Researchers at Princeton have created a computer vision system capable of mining Google Street View and OpenStreetMap, creating a training set for autonomous driving systems. OpenAI released a similar training set as part of its Universe platform, allowing an autonomous driving system to train on Grand Theft Auto V.
Why it's important: While these cannot fully replicate real on-the-road data, these data sets and their progeny will allow autonomous systems to learn faster, and with scenarios that they may only rarely encounter, such as complex intersections. Importantly, as these are also being open-sourced, this is a big step towards democratizing and demonetizing the data we use to create autonomous systems. Look for an explosion in autonomous driving systems beyond Google, Tesla, and the major automakers who are able to afford the large fleets needed to acquire real data. Join the Discussion
Spotted by Marissa Brassfield / Written by Jason Goodwin
What is Abundance Insider?
This email is a briefing of the week's most compelling, abundance-enabling tech developments, curated by Marissa Brassfield in preparation for Abundance 360. Read more about A360 below.
Want more conversations like this?
At Abundance 360, Peter's 250-person executive mastermind, we teach the metatrends, implications and unfair advantages for entrepreneurs enabled by breakthroughs like those featured above. We're looking for CEOs and entrepreneurs who want to change the world. The program is highly selective. If you'd like to be considered, apply here.
Know someone who would benefit from getting Abundance Insider? Send them to this link to sign up.
P.S. I'm launching an online course with SUCCESS Magazine called Xponential Advantage. It's aimed to inspire, educate and guide a new breed of "Exponential Entrepreneurs," and is an expansion of my core content from Abundance and BOLD, the keynotes I give to Fortune 500 executive teams, and some of the material I teach executives who attend Singularity University. These are the areas I truly believe an exponential entrepreneur can leverage to have a billion-person impact. Learn more about the course here.
PHD Ventures , 800 Corporate Pointe, Suite 350, Culver City, CA 90230
No comments:
Post a Comment